Introduction
Traditional language models generate responses based solely on pre-learned patterns and data acquired during their training phase. However, this approach has limitations, particularly when handling queries requiring specific, real-time, or extensive knowledge beyond the model’s training data.
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) addresses these limitations by incorporating external knowledge retrieval into the generation process, ensuring that responses are informed by the most relevant and up-to-date information. This makes RAG particularly useful for applications requiring high accuracy and contextual depth.
How RAG Works: An Overview
RAG is a hybrid system consisting of two main components:
- Retriever Component: Searches a knowledge base or dataset for relevant information based on the user query.
- Generator Component: Uses the retrieved information to generate an informed and coherent response.
By integrating both components, RAG improves response accuracy, making AI models more reliable and capable of handling complex queries.
RAG Architecture: A Two-Component System
1. Retriever Component
The retriever is responsible for fetching relevant documents or data points that can help generate a response. It works by matching the user query with existing knowledge stored in a database.
Types of Retrievers:
- Dense Retrievers: Use deep learning-based embeddings to capture the semantic meaning of queries and documents, improving results when understanding context is more important than exact words.
- Sparse Retrievers: Use keyword-matching techniques like TF-IDF or BM25, making them effective for retrieving documents with specific words or phrases.
- Hybrid Retrievers: Combine both dense and sparse methods for a balanced approach, leveraging deep understanding while maintaining precise keyword matching.
2. Generator Component
The generator component is a language model responsible for crafting responses based on the retrieved information. It does not generate responses in isolation but rather refines its output using the retrieved context, ensuring a well-informed and contextually accurate response.
Key Functions:
- Synthesizes retrieved knowledge with the input query.
- Enhances accuracy by reducing reliance on static training data.
- Produces coherent, informative, and precise responses.
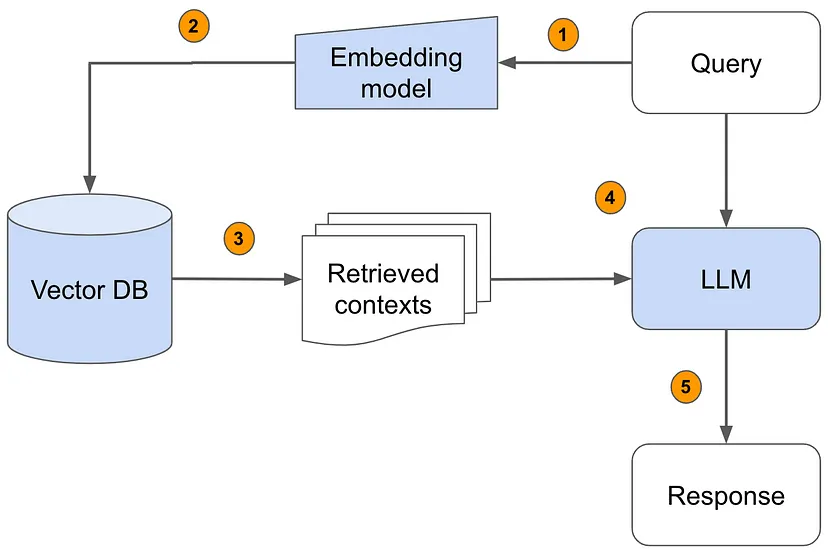
The RAG Workflow: Step-by-Step
- Query Processing: The user inputs a query (e.g., a question or request for information).
- Embedding Conversion: The query is transformed into a numerical representation (vector) via an embedding model.
- Vector Database Retrieval: The system searches for relevant contexts in a precomputed vector database and retrieves the most similar or relevant pieces of information.
- Contextual Augmentation: Retrieved data is passed to the language model to provide enriched context.
- Response Generation: The model synthesizes information from both its internal knowledge and the retrieved content to generate an accurate response.
- Final Output: The response is delivered to the user, providing a more informed and detailed answer.
Applications of RAG
1. Enhancing Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
- Customer Support: RAG-powered bots retrieve product information and FAQs, improving accuracy in customer interactions.
- Personal Assistants: AI assistants leverage real-time data, such as weather updates and news, for relevant responses.
2. Improving Automated Content Generation
- Journalism & Content Creation: AI tools can fetch real-time facts and references, enhancing content quality.
- Marketing & Copywriting: RAG generates creative and accurate product descriptions by referencing product specs and user reviews.
3. Advanced Question-Answering Systems
- Education: AI tutors use RAG to provide detailed explanations by pulling in relevant educational content.
- Research & Academia: Researchers leverage RAG to extract summaries and insights from vast scientific databases.
4. Industry-Specific Uses
- Healthcare: AI-powered medical tools retrieve research papers and case studies to assist doctors in diagnosis and treatment.
- Legal Research: RAG-based systems extract relevant case laws and legal precedents for lawyers and legal analysts.
- Translation Services: Context-aware translations benefit from retrieval-based insights to ensure linguistic accuracy.
Benefits of Using RAG
- Enhanced Accuracy: By retrieving real-world data, RAG significantly improves the factual correctness of generated responses.
- Contextual Awareness: Unlike static models, RAG adapts to real-time information, making responses more dynamic.
- Flexibility: Works across various domains, from customer service to legal research, improving AI adaptability.
- Scalability: Large-scale applications benefit from RAG’s ability to handle vast amounts of information efficiently.
Challenges and Limitations of RAG
1. Complexity
Integrating retrieval with generation adds complexity to system design, requiring advanced optimization techniques.
2. Latency
Retrieval processes introduce delays, impacting response time, which can be critical in real-time applications like chatbots.
3. Data Quality & Reliability
The effectiveness of RAG depends on the quality and reliability of external data sources. Incorrect or biased data can affect the accuracy of responses.
4. Context Window Limitations
The model may struggle if the retrieved information exceeds its input capacity, leading to truncated or incomplete responses.
Potential Future Enhancements
- Better Retrieval Mechanisms: Improving retrieval models to enhance response relevance.
- Adaptive Learning: Enabling RAG systems to learn from user feedback to refine responses over time.
- Cross-Modal Retrieval: Expanding retrieval beyond text to include images, videos, and audio for richer AI interactions.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Keeping databases continuously updated to ensure access to the latest information.
- Personalization: Using user history and preferences to provide tailored and more relevant responses.
Let’s see the practical implementation
from llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.llms.gemini import Gemini
import google.generativeai as genai
from IPython.display import display, Markdown
from llama_index.core import ServiceContext
from llama_index.core import StorageContext, load_index_from_storage
from llama_index.embeddings.gemini import GeminiEmbedding
# Install required packages
# pip install llama-index-embeddings-gemini
# If any error occurs while loading llama_index modules, perform the following steps:
# In a new terminal:
# pip uninstall llama-index # Remove any possible global install
# python -m venv venv
# source venv/bin/activate
# pip install llama-index --upgrade --no-cache-dir --force-reinstall
# Configure Google Gemini API
google_api_key = "YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY"
genai.configure(api_key=google_api_key)
# List available models from Google Gemini
for models in genai.list_models():
print(models)
# Load documents from the 'data' directory
documents = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data")
doc = documents.load_data()
# Display the first document's text
print(doc[0].text)
# Initialize Gemini Embedding Model
gemini_embed_model = GeminiEmbedding(model_name="models/text-embedding-004")
# Initialize Gemini LLM Model
model = Gemini(model_name="gemini-pro", api_key=google_api_key)
# Set up service context with embedding model and chunk size
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(
llm=model, embed_model=gemini_embed_model, chunk_size=800, chunk_overlap=20
)
# Apply global settings
from llama_index.core import Settings
Settings.llm = model
Settings.embed_model = gemini_embed_model
Settings.chunk_size = 800
Settings.chunk_overlap = 20
# Create a Vector Store Index for RAG-based retrieval
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(doc)
index.storage_context.persist()
# Create a query engine to retrieve relevant document contexts
query_engine = index.as_query_engine()
# Perform a query using RAG
response = query_engine.query("Tell me about Akshay")
print(response.response)
# Install additional required packages
# %pip install llama-index-llms-gemini llama-index
# Initialize a different Gemini model for direct LLM queries
llm = Gemini(
model="models/gemini-1.5-flash",
api_key=google_api_key, # Uses GOOGLE_API_KEY env var by default
)
# Generate a response using the Gemini model
resp = llm.complete("Write a poem about a magic backpack")
print(resp)
How to Use This Code
- Replace
"YOUR_GOOGLE_API_KEY"with your actual Google Gemini API key. - Ensure you have the required Python packages installed (
llama-index,google-generativeai). - Store your text documents inside a folder named
./databefore running the code. - This script:
- Reads and indexes documents.
- Uses Gemini embeddings to store them in a vector database.
- Implements Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) to generate responses based on the retrieved documents.
- Uses
GeminiLLM directly to generate answers.
1. Understanding the Code
Step 1: Install Required Libraries
pythonCopyEdit%pip install llama-index-embeddings-gemini llama-index
This installs the necessary packages, including:
llama-index(previously GPT Index) for efficient document indexing and retrieval.llama-index-embeddings-geminito use Google Gemini embeddings for text processing.
Step 2: Import Required Modules
pythonCopyEditfrom llama_index.core import SimpleDirectoryReader, VectorStoreIndex
from llama_index.llms.gemini import Gemini
import google.generativeai as genai
from IPython.display import display, Markdown
from llama_index.core import ServiceContext
from llama_index.core import StorageContext, load_index_from_storage
from llama_index.embeddings.gemini import GeminiEmbedding
SimpleDirectoryReader: Reads documents from a folder (./data).VectorStoreIndex: Creates an index for document retrieval.GeminiEmbedding: Converts text into numerical vectors.Gemini: Uses Google’s Gemini LLM for response generation.ServiceContext: Stores configuration settings like embedding model and chunk sizes.StorageContext: Manages persistent storage for the document index.
Step 3: API Configuration
pythonCopyEditgoogle_api_key = "YOUR_API_KEY"
genai.configure(api_key=google_api_key)
This configures Google Gemini API using your API key.
To list all available Gemini models:
pythonCopyEditfor models in genai.list_models():
print(models)
Step 4: Load Documents
pythonCopyEditdocuments = SimpleDirectoryReader("./data")
doc = documents.load_data()
- Reads all documents in the
./datafolder. - Stores the content in a list called
doc.
To check the text of the first document:
pythonCopyEditdoc[0].text
Step 5: Create an Embedding Model
pythonCopyEditgemini_embed_model = GeminiEmbedding(model_name="models/text-embedding-004")
This initializes Google’s embedding model, which converts text into numerical vectors for efficient similarity searches.
!!!! Important note
In updated version service context is updated. So perform step 7 directly
Step 6: Configure LLM and Indexing Settings
pythonCopyEditmodel = Gemini(models="gemini-pro", api_key=google_api_key)
service_context = ServiceContext.from_defaults(
llm=model,
embed_model=gemini_embed_model,
chunk_size=800,
chunk_overlap=20
)
- Uses Gemini Pro as the LLM.
- Embedding model is set to GeminiEmbedding.
- Chunk size (
800) defines the max token length for each document chunk. - Chunk overlap (
20) ensures slight overlap to maintain context.
Step 7: Global Settings for LlamaIndex
pythonCopyEditfrom llama_index.core import Settings
Settings.llm = model
Settings.embed_model = gemini_embed_model
Settings.chunk_size = 800
Settings.chunk_overlap = 20
Sets the default LLM, embedding model, and chunking parameters.
Step 8: Create a Vector Store Index
pythonCopyEditindex = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(doc)
index.storage_context.persist()
- Converts the documents into an indexed vector database for efficient retrieval.
- Saves the index for future use.
Step 9: Query the Index
pythonCopyEditquery_engine = index.as_query_engine()
response = query_engine.query('tell me about Akshay')
response.response
- Converts the index into a query engine.
- Searches for relevant context and passes it to the LLM.
- Generates a response based on retrieved data.
Step 10: LLM Direct Query (No Retrieval)
pythonCopyEditllm = Gemini(
model="models/gemini-1.5-flash",
api_key="YOUR_API_KEY"
)
resp = llm.complete("Write a poem about a magic backpack")
print(resp)
- This directly queries the Gemini LLM without document retrieval.
2. How RAG is Implemented in This Code?
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
RAG is a technique where a retrieval model fetches relevant information from stored data, and an LLM generates a response using this retrieved context.
RAG Implementation in this Code:
- Document Processing & Storage
- The
SimpleDirectoryReaderreads documents. - The
VectorStoreIndexindexes them usingGeminiEmbedding.
- The
- Retrieval Phase
- The
query_engine.query()function searches for relevant document chunks based on user queries.
- The
- Generation Phase
- The retrieved context is fed into the Gemini LLM to generate a context-aware response.
- Final Response
- The LLM generates an answer using retrieved information + its own knowledge.
This combination of retrieval and generation ensures:
✅ Factually correct answers (retrieved from indexed data).
✅ Reduced hallucinations (LLM does not guess).
✅ Context-aware responses (better accuracy).
3. RAG vs. Direct LLM Query
| Feature | RAG | Direct LLM Query |
|---|---|---|
| Retrieves from documents | ✅ | ❌ |
| Uses embeddings for retrieval | ✅ | ❌ |
| More context-aware responses | ✅ | ❌ |
| Better factual accuracy | ✅ | ❌ |
Conclusion
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) represents a significant advancement in AI, allowing language models to generate responses that are not only well-formed but also enriched with up-to-date, external knowledge. Its applications span across industries, improving everything from customer service chatbots to legal and medical research tools.
Despite its challenges, ongoing advancements in retrieval techniques, adaptive learning, and multimodal retrieval promise an even more powerful and efficient RAG system in the future. As AI continues to evolve, RAG will play a crucial role in making machine-generated content more accurate, relevant, and insightful.