Introduction
Generative AI (GenAI) is reshaping industries by enabling the development of intelligent, self-learning systems. However, moving from a prototype to a scalable, production-ready AI solution presents unique challenges. This guide outlines the key strategies, technologies, and best practices for building robust, AI-driven agent applications that can thrive in real-world environments.

The Future of Agentic Development
AI agents are evolving far beyond basic automation. Today, businesses are embracing Agent-as-a-Service (AaaS) models, allowing flexible, modular, and scalable deployment of intelligent agents. These agents can emulate human representatives, enhancing workflows across customer service, operations, HR, and more.
Core Concepts Covered in This Guide
🧠 Direct Prompting
🔍 Embeddings & Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
🧪 LLM Evaluations & Performance Testing
🎯 Fine-Tuning Custom AI Models
📚 Mastering Key LLM Techniques
1. Direct Prompting: The Simplest AI Interaction
One of the most accessible ways to interact with a Large Language Model (LLM) is direct prompting—you ask a question, and the AI returns a response.
💬 Example: AI Chatbot for E-Commerce
User: “Where is my order?”
AI: “Please provide your order ID, and I’ll check the status for you.”
🔧 Business Use Cases:
Customer Support Automation
AI-Powered Workflow Optimization
Content Generation & Personalization
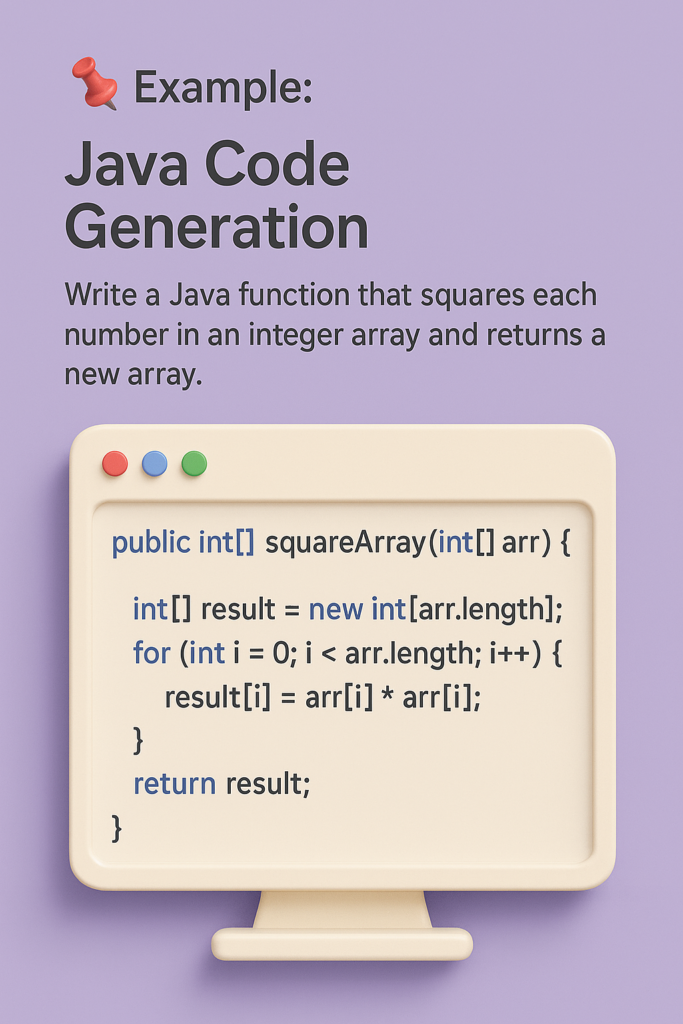
📌 Example: Java Code Generation Prompt: Write a Java function that squares each number in an integer array and returns a new array.
public int[] squareArray(int[] arr) {
int[] result = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
result[i] = arr[i] * arr[i];
}
return result;
}
2. Evaluating LLM Responses (EVALs)
Traditional software testing yields deterministic results. In contrast, LLM outputs vary, so evaluating their performance requires more nuanced metrics.
⚖️ Comparison Table:
| Aspect | Traditional Software | LLM-Based AI |
|---|---|---|
| Output Consistency | Fixed | Variable |
| Evaluation Criteria | Pass/Fail | Relevance & Accuracy |
| Testing Techniques | Unit Testing | AI-Based EVALs |
Evaluation Techniques for AI Models
Who evaluates AI responses—and how—is critical for building trust in AI systems.
✅ Common Evaluation Methods:
Automated Evaluation: Uses metrics like BLEU, ROUGE, or GPTScore.
Human Evaluation: Experts judge responses based on relevance and coherence.
Hybrid Evaluation: Combines both human and AI scoring.
Hands-On Example: AI Evaluation Using DeepEval
from deepeval import assert_test
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
from deepeval.metrics import AnswerRelevancyMetric
def test_answer_relevancy():
answer_relevancy_metric = AnswerRelevancyMetric(threshold=0.5)
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input=”How do I reset my corporate email password?”,
actual_output=”Visit the IT portal and follow password recovery steps. Contact support if needed.”,
retrieval_context=[“To reset your password, visit the IT portal and follow the steps.”]
)
assert_test(test_case, [answer_relevancy_metric])
test_answer_relevancy()
Learn more, click on below image to see more details about LLM Evaluation 
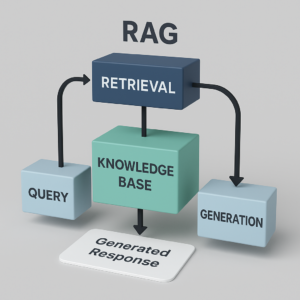
3. RAG
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is an AI framework that combines a language model with a retrieval system. Instead of generating responses purely from its internal knowledge, the model first retrieves relevant documents from an external knowledge base and then generates a response using both the query and the retrieved information. This improves accuracy, keeps outputs up-to-date, and helps handle questions about topics the model hasn’t been explicitly trained on.
Key features:
Combines retrieval + generation.
Enhances factual accuracy.
Useful for open-domain question answering, chatbots, and knowledge-intensive tasks
Learn more about RAG: click on below image for learn more
✨ Final Thought
Building next-gen AI agents requires a balance of technical precision, strategic design, and continuous evaluation. With the right approach, these agents can transform how businesses operate and innovate.